-
1. Overview
-
1-1. Computer Security Concepts
-
1-2. A Model for Computer Security
-
2. Threats, Attacks, and Assets
-
2-1. Threats and Attacks
-
2-2. Threats and Assets
-
3. Security Functional Requirements
-
4. Fundamental Security Design Principles
-
5. Attack Surfaces and Attack Trees
-
5-1. Attack Surfaces
-
5-2. Attack Trees
-
6. Computer Security Strategy
-
7. Standards
1. Overview
1-1. Computer Security Concepts
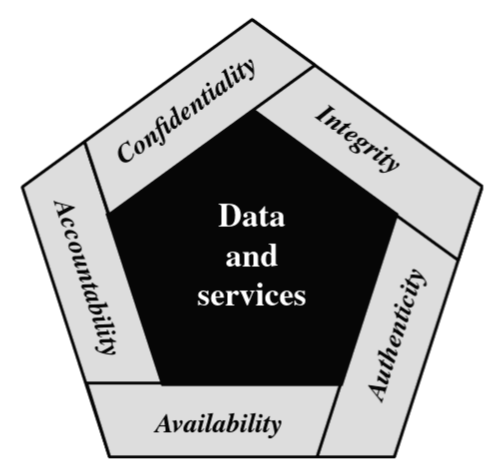
Computer Security: Measures and Controls that ensure confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information system and information being processed, stored, and communicated.
Key objectives of computer Security:
|
Confidentiality* |
Preserving autorized restrictions on information access |
|
Integrity* |
Guarding against improper information modification or destruction |
|
Availability* |
Ensuring timely and reliable access to and use information |
|
Authenticity |
The property of being genuine and being able to be verified and trusted |
|
Accountability |
The Security goal that generates the requirement for actions of an entity to be traced uniquely to that entity |
we use three levels of impact on organizations or individuals should there be a breach security
: Low, Moderate, High
1-2. A Model for Computer Security
System Resources(or Assets):
| Hardware | Including computer systems and other data processing, data storage, and data communications devices |
| Software | Including the operating system, system utilities, and applications |
| Data | Including files and databases as well as security-related data(ex. password files) |
| Communication facilities and networks | Local and wide area network communication links, bridges, routers, and so on. |
Computer Security Terminology:
| Adversary(threat agent) | What conducts or has the intent to conduct detrimental activities |
| Attack | Any kind of malicious activity that threatens information system or information itself |
| Countermeasure | A device or techniques that reduce a threat, a vulnerability, an attack, etc |
| Risk | A measure of the extent to which an entity is threatened by a potential circumstance or event |
| Security Policy | A set of criteria for the provision of security services |
| Threat | Any circumstance or event with the potential to adversary impact individuals, organizations, or the Nation |
| Vulnerability | Weakness in an information system, internal controls, implementations, etc |
Attacks and Relationships:
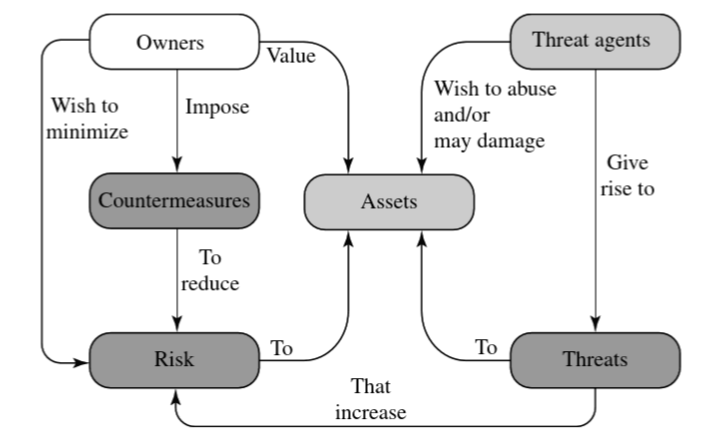
Attacks can be classified -> Active/Passive, Inside/Outside
2. Threats, Attacks, and Assets
2-1. Threats and Attacks
- Unauthorized Disclosure
Threat to confidentiality
|
Exposure |
Sensitive data are directly released to an unauthorized entity |
|
Interception |
An unauthorized entity directly accesses sensitive data traveling between authorized sources and destinations |
|
Inference |
A threat action whereby unauthorized entity indirectly accesses sensitive data |
|
Intrusion |
An unauthorized entity gains access to sensitive data by circumventing a system's security protections |
- Deception
Threat to integrity
|
Masquerade |
An unauthorized entity gains access to a system or performs a malicious act by posing as an authorized entity |
|
Falsification |
Altering or replacing of valid data or introducing of false data |
|
Repudiation |
An entity devices another by falsely denying responsibility for an act |
- Disruption
Threat to avaliability or system integrity
|
Incapacitation |
Preventing or interrupting system opration by disabling a system component |
|
Corruption |
Undesirably altering system operation by adversely modifying system functions or data |
|
Obstruction |
A threat action that interrupts delievery of system services by hindering system opreation |
- Usurpation
Threat to system integrity
|
Misappropriation |
An entity assumes unauthorized logical or physical control of a system resource |
|
Misuse |
Causes a system component to perform a function or service that detrimental to system security |
2-2. Threats and Assets
| Availability | Confidentiality | Integrity | |
| Hardware | Equipment is stolen or disabled | An unencrypted USB drive is stolen | |
| Software | Programs are deleted | An unauthorized copy of software made | A working program is modified. |
| Data | Files are deleted | An unauthorized read of data is performed | Existing files are modified. |
| Communication lines and networks |
Messages are destroyed or deleted. Communication lines and networks are rendered unavailable. |
Messages are read. The traffic pattern is observed. |
Messages are modified. False messages are fabricated. |
3. Security Functional Requirements
|
Access Control |
|
Awareness and training |
|
Audit and Accountability |
|
Certification, Accreditation, and Security Assessments |
|
Configuration Management |
|
Contingency planning |
|
Identification and Authentication |
|
Incident Response |
|
Maintenance |
|
Media Protection |
|
Physical and Environmental Protection |
|
Planning |
|
Personal Security |
|
Risk Assessment |
|
Systems and Services Acquisition |
|
System and Communications Protection |
|
System and Information Integrity |
4. Fundamental Security Design Principles
|
Economy of Mechanism |
|
Fail-safe Defaults |
|
Complete Mediation |
|
Open Design |
|
Separation of Privilege |
|
Least Privilege |
|
Least Common Mechanism |
|
Psychological Acceptability |
|
Isolation |
|
Encapsulation |
|
Modularity |
|
Layering |
|
Least Astonishment |
5. Attack Surfaces and Attack Trees
5-1. Attack Surfaces
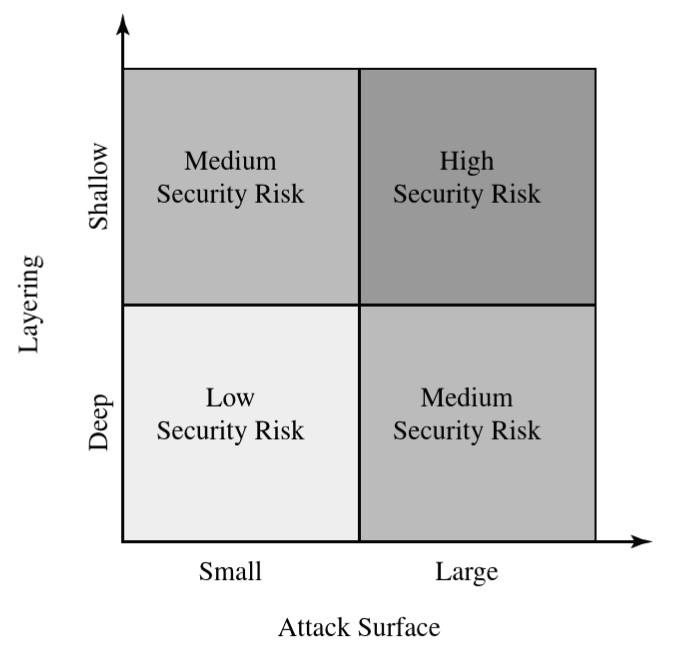
An attack surface analysis is a useful technique for assessing scale and severity of threats to a system
: Network, Software, Human attack surface, etc
5-2. Attack Trees
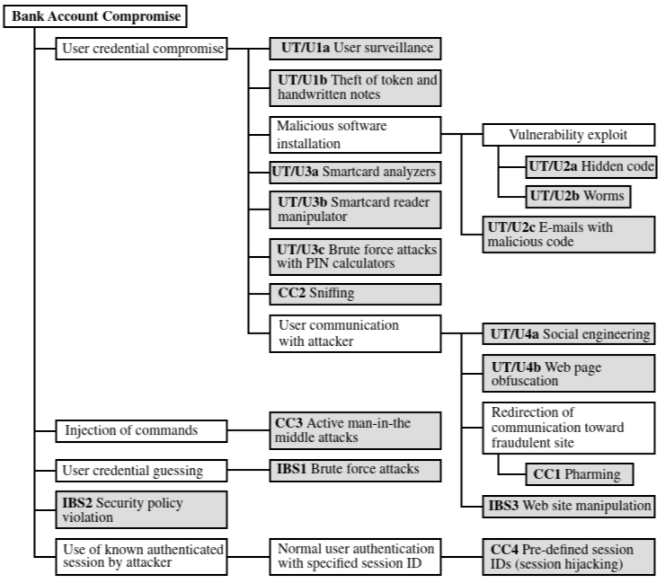
An attack tree is a branching, hierarchical data structure that represents a set of potential techniques for exploiting security vulnerabilities.
6. Computer Security Strategy
|
Specification/policy |
What is the security scheme supposed to do? |
Easy of use VS Security Cost of Security VS Cost of failure and recovery |
|
Implementation/mechanisms |
How does it do it? |
Prevention Detection Response Recovery |
|
Correctness/assurance |
Dose it really work? |
Assurance Evaluation |
7. Standards
|
NIST |
U.S. federal agency |
|
ISOC |
Professional membership society |
|
ITU-T |
United Nation agency |
|
ISO |
World wide federation of national standards bodies |
Amazon.com
Enter the characters you see below Sorry, we just need to make sure you're not a robot. For best results, please make sure your browser is accepting cookies.
www.amazon.com
1. Overview
1-1. Computer Security Concepts
Computer Security: Measures and Controls that ensure confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information system and information being processed, stored, and communicated.
Key objectives of computer Security:

|
Confidentiality* |
Preserving autorized restrictions on information access |
|
Integrity* |
Guarding against improper information modification or destruction |
|
Availability* |
Ensuring timely and reliable access to and use information |
|
Authenticity |
The property of being genuine and being able to be verified and trusted |
|
Accountability |
The Security goal that generates the requirement for actions of an entity to be traced uniquely to that entity |
we use three levels of impact on organizations or individuals should there be a breach security
: Low, Moderate, High
1-2. A Model for Computer Security
System Resources(or Assets):
| Hardware | Including computer systems and other data processing, data storage, and data communications devices |
| Software | Including the operating system, system utilities, and applications |
| Data | Including files and databases as well as security-related data(ex. password files) |
| Communication facilities and networks | Local and wide area network communication links, bridges, routers, and so on. |
Computer Security Terminology:
| Adversary(threat agent) | What conducts or has the intent to conduct detrimental activities |
| Attack | Any kind of malicious activity that threatens information system or information itself |
| Countermeasure | A device or techniques that reduce a threat, a vulnerability, an attack, etc |
| Risk | A measure of the extent to which an entity is threatened by a potential circumstance or event |
| Security Policy | A set of criteria for the provision of security services |
| Threat | Any circumstance or event with the potential to adversary impact individuals, organizations, or the Nation |
| Vulnerability | Weakness in an information system, internal controls, implementations, etc |
Attacks and Relationships:

Attacks can be classified -> Active/Passive, Inside/Outside
2. Threats, Attacks, and Assets
2-1. Threats and Attacks
- Unauthorized Disclosure
Threat to confidentiality
|
Exposure |
Sensitive data are directly released to an unauthorized entity |
|
Interception |
An unauthorized entity directly accesses sensitive data traveling between authorized sources and destinations |
|
Inference |
A threat action whereby unauthorized entity indirectly accesses sensitive data |
|
Intrusion |
An unauthorized entity gains access to sensitive data by circumventing a system's security protections |
- Deception
Threat to integrity
|
Masquerade |
An unauthorized entity gains access to a system or performs a malicious act by posing as an authorized entity |
|
Falsification |
Altering or replacing of valid data or introducing of false data |
|
Repudiation |
An entity devices another by falsely denying responsibility for an act |
- Disruption
Threat to avaliability or system integrity
|
Incapacitation |
Preventing or interrupting system opration by disabling a system component |
|
Corruption |
Undesirably altering system operation by adversely modifying system functions or data |
|
Obstruction |
A threat action that interrupts delievery of system services by hindering system opreation |
- Usurpation
Threat to system integrity
|
Misappropriation |
An entity assumes unauthorized logical or physical control of a system resource |
|
Misuse |
Causes a system component to perform a function or service that detrimental to system security |
2-2. Threats and Assets
| Availability | Confidentiality | Integrity | |
| Hardware | Equipment is stolen or disabled | An unencrypted USB drive is stolen | |
| Software | Programs are deleted | An unauthorized copy of software made | A working program is modified. |
| Data | Files are deleted | An unauthorized read of data is performed | Existing files are modified. |
| Communication lines and networks |
Messages are destroyed or deleted. Communication lines and networks are rendered unavailable. |
Messages are read. The traffic pattern is observed. |
Messages are modified. False messages are fabricated. |
3. Security Functional Requirements
|
Access Control |
|
Awareness and training |
|
Audit and Accountability |
|
Certification, Accreditation, and Security Assessments |
|
Configuration Management |
|
Contingency planning |
|
Identification and Authentication |
|
Incident Response |
|
Maintenance |
|
Media Protection |
|
Physical and Environmental Protection |
|
Planning |
|
Personal Security |
|
Risk Assessment |
|
Systems and Services Acquisition |
|
System and Communications Protection |
|
System and Information Integrity |
4. Fundamental Security Design Principles
|
Economy of Mechanism |
|
Fail-safe Defaults |
|
Complete Mediation |
|
Open Design |
|
Separation of Privilege |
|
Least Privilege |
|
Least Common Mechanism |
|
Psychological Acceptability |
|
Isolation |
|
Encapsulation |
|
Modularity |
|
Layering |
|
Least Astonishment |
5. Attack Surfaces and Attack Trees
5-1. Attack Surfaces
An attack surface analysis is a useful technique for assessing scale and severity of threats to a system
: Network, Software, Human attack surface, etc

5-2. Attack Trees
An attack tree is a branching, hierarchical data structure that represents a set of potential techniques for exploiting security vulnerabilities.

6. Computer Security Strategy
|
Specification/policy |
What is the security scheme supposed to do? |
Easy of use VS Security Cost of Security VS Cost of failure and recovery |
|
Implementation/mechanisms |
How does it do it? |
Prevention Detection Response Recovery |
|
Correctness/assurance |
Dose it really work? |
Assurance Evaluation |
7. Standards
|
NIST |
U.S. federal agency |
|
ISOC |
Professional membership society |
|
ITU-T |
United Nation agency |
|
ISO |
World wide federation of national standards bodies |
Amazon.com
Enter the characters you see below Sorry, we just need to make sure you're not a robot. For best results, please make sure your browser is accepting cookies.
www.amazon.com
